Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Acridine
Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Acridine
Acridine is a three-membered fused heterocyclic system containing Nitrogen as a heteroatom at the 10th position. Two benzene rings are fused to the "b" and "e" sides of pyridine. Other names for acridine are 2,3-Benzoquinoline and Dibenzo[b,e]pyridine.
Physical properties:
Colour: white
State: powder(solid)
Melting point: 106 - 110 oC
Boiling point: 344.86 oC
Solubility: Slightly soluble in hot water and soluble in organic solvents.
Structure and Aromaticity:
Acridine is a planar molecule, all atoms are sp2 hybridised. Unhybridised p-orbitals sidewise overlap to form pi bonds. Acridine contains seven double bonds and 14 delocalised pi electrons, following the huckles rule(4n+2)pi electrons (where n=3). Hence acridine is aromatic.
Synthesis of Acridine:
1. Ulmann synthesis:
2-chlorobenzoic acid reacts with aniline in the presence of sodium hydroxide give diphenylamino-2-carboxylic acid(DPCA).
(i) DPCA treated with strong acid give 9(10H)-acridinone, which upon reduced with Na in ethanol gives 9,10-dihydroacridine.
(ii) DPCA reacted with phosphorous oxychloride give 9-chloro-9,10-dihydroacridine, which upon reduced with hydrogen and nickel gives 9,10-dihydroacridine.
The formed 9,10-dihydroacridine upon oxidation give acridine.
2. Bernthsen acridine synthesis:
Diarylamine heated with a carboxylic acid or acid anhydride in the presence of Zinc chloride gives 9-substituted acridine.
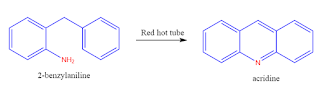
3. From 2-benzyl aniline:
2-benzyl aniline passed through a red hot tube gives acridine.
Electrophilic addition reactions to 'N' of Acridine.
1. Protonation:
Acridine reacts with acids and gives acridinium salts.
Electrophilic substitution reactions:
Electrophilic substitution reactions of acridine give a mixture of 2-substituted and 2,7-disubstituted derivatives.
1. Nitration:
Acridine upon nitration gives a mixture of 2-nitro and 2,7-dinitro acridine.
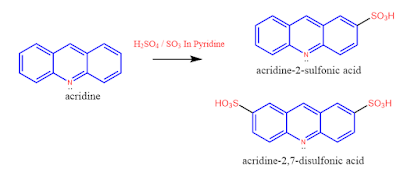
2. Sulphonation:
Acridine upon sulphation gives acridine-2-sulphonic acid and acridine-2,7-sulphonic acid.
3. Halogenation:
Acridine upon halogenation gives 2-halo and 2,7-dihalo acridine.
Acridine readily reacts with nucleophiles. nucleophilic reactions take place at the 9th position.
Chichibabin reaction: Acridine reacts with Sodamide in liquid ammonia leading to 9-aminoacridine.
Oxidation reactions:
1. Acridine oxidized with sodium dichromate in acetic acid gives 9-(10H)-acridine.
2. Acridine is oxidised by potassium permanganate in an alkaline medium gives quionoline-2,3-dicarboxylic acid.
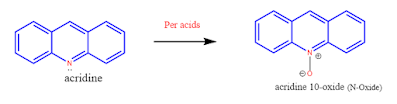
3. Acridine reacts with peroxy acids and gives acridine-N-oxides.
Reduction reactions:
1. Acridine reduced with hydrogen and pt as catalyst gives 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroacridine.
2. Acridine reduced with hydrogen and Ni as Catalyst or Zinc in Hcl gives 9,10-dihydroacridine.
3. Acridine reduced with Na in liquid ammonia gives 1,4,5,8-tetrahydroacridine.
Medicinal uses:
Drugs containing Acridine ring:
1. Tacrine: Anticholinesterase drug used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
2. 9-Aminoacridine: Slow-acting germicide, used as an antiseptic and disinfectant. also used in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis.
3. Quinacrine: used in the treatment of malaria and tapeworm infections. also used in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis and giardiasis.
4. Proflavine: A topical antiseptic agent used to prevent infections.
References (Latest editions):
Heterocyclic chemistry by Raj K. Bansal.
Heterocyclic chemistry by T.L. Gilchrist.
Organic chemistry by Morrison and Boyd.
A textbook of organic chemistry - Arun Bahl. B.S. Bahl.


























Comments
Post a Comment