Relative aromaticity and reactivity of Pyrrole, Furan, and Thiophene
Relative aromaticity and reactivity of Pyrrole, Furan, and Thiophene
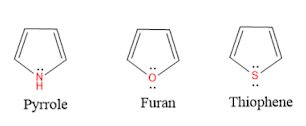
Relative aromaticity of Pyrrole, Furan, and Thiophene:
Aromatic compounds are cyclic hydrocarbon compounds contains alternate double and single bonds.pi electrons are delocalised inside the ring enhance the stability of the compound. Pyrrole, thiophene and furan are the heterocyclic aromatic compounds contain nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen as heteroatom respectively. the lone pair of electrons on heteroatom get involved and participate in aromaticity.
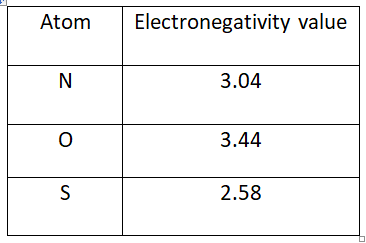
In order to know the order of aromaticity in pyrrole, furan and thiophene we need to about electronegativity of nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom which drags the shared pair of electrons towards it. Electronegative values of nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur are given below.
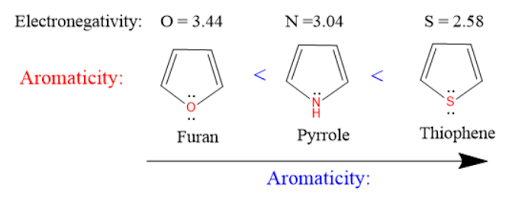
High electronegative means it tightly holds the electrons, especially lone pair of electrons present on an atom and hinders the delocalisation of pi electrons within the ring system. Aromatic character directly depends on delocalisation pi electrons. high electronegative atoms hinder pi-electron delocalisation hence the respective molecule aromaticity is decreased.
Furan contains oxygen atom has high electronegative value(3.44) which is less aromatic than pyrrole which contains nitrogen atom has electronegative value(3.04), which in turn less aromatic than thiophene which contains sulfur atom has electronegative value(2.58).
Aromaticity : Thiophene > Pyrrole > Furan
Relative reactivity of Pyrrole, Furan, and Thiophene:
More aromatic character means more stable it is. and less reactive.
Furan has less aromatic character than pyrrole and thiophene, hence furan is more reactive than pyrrole and thiophene. Pyrrole is less aromatic than thiophene and more aromatic than furan. hence pyrrole is more reactive than thiophene and less reactive than furan. Thiophene has more aromatic character than pyrrole and furan. hence thiophene is more stable and less reactive than pyrrole and furan.
Reactivity: Thiophene <Pyrrole <Furan
L









Comments
Post a Comment