Synthesis, Reactions and Medicinal Uses of Pyrrole
Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Pyrrole
Pyrrole is a five-membered heterocyclic compound having one nitrogen atom as a heteroatom.
Physical properties:
Colour : colorless
State : liquid
Boiling point : 131oC
Melting point : -23oC
Solubility : Insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents
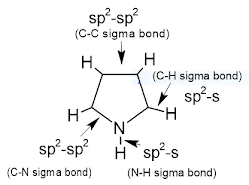
Structure & Aromaticity:
All atoms in the pyrrole ring are sp2 hybridised, so the pyrrole contains a planar ring structure. the sp2 hybrid orbitals overlap with each other and with "s" atomic orbital of the five hydrogens forming C-C, C-N, C-H, and N-H sigma bonds. all these sigma bonds lie in one plane.
Pyrrole also has unhybridized p orbitals and these are perpendicular to the plane of the ring. each p orbital on carbon atom contains one electron and the p orbital on nitrogen contains lone pair of electrons(two electrons). the p orbital overlap to form delocalized pi molecular orbital. Pyrrole shows aromaticity because the resulting pi molecular orbital (which contain 6 electrons) satisfies the Huckel's rule (n=1 in 4n+2).
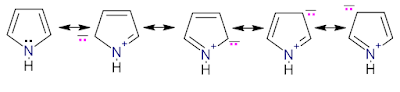
Resonance structures:
Acidity: Pyrrole is a weak acid (pka is 16.5). Pyrrolyl anion is a strong base.
Basicity: Pyrrole is a weak base (pkb is 13.6).
Synthesis:
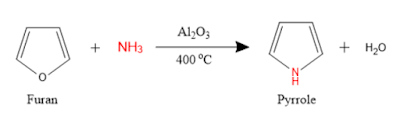
1. From furan: Industrially pyrrole is synthesized by passing a mixture of furan and ammonia over alumina (catalyst) at high temperatures.
2. Paal-Knorr synthesis: Condensation of 1,4- Dicarbonyl compounds with ammonia or primary amines to give pyrrole. the reaction is conducted under neutral or weakly acidic conditions.
3. Hantzsch synthesis: Reaction of β-ketoesters with ammonia or primary amines and α-halo ketones give substituted pyrroles
Mechanism:
4. Knorr synthesis: It is a condensation reaction of α-amino ketone and a compound containing an electron-withdrawing group to a carbonyl group in the presence of zinc and glacial acetic acid gives substituted pyrrole.
Mechanism:
Electrophilic substitution reactions:
Electrophile attack at 2nd position gives more resonance structures than electrophile attack at the 3rd position. More resonance structures mean more stable it is.
So, electrophilic substitution reactions take place 2nd position in pyrrole.
Substitution at "C":
1. Halogenation: Pyrrole reacts with halogens to give 2-Halo pyrrole(under controlled conditions). excess halogenation gives tetra halo pyrrole.
2. Nitration: Pyrrole reacts with concentrated nitric acid in acetic acid gives 2-nitro pyrrole.
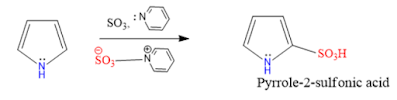
3. Sulphonation: Pyrrole treated with sulfur trioxide in pyridine gives Pyrrole-2-sulfonic acid.
4. Acylation: Pyrrole reacts with Acetic anhydride at 200 oC give 2-Acyl pyrrole.
Substitution at "N":
5. N-Alkylation: pyrrole reacts with an alkyl halide in Liq. ammonia to give N-alkyl pyrrole.
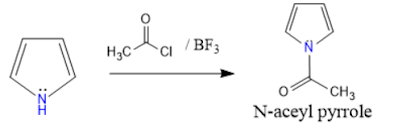
6. N-Acetylation: pyrrole reacts with Acetyl chloride and boron trifluoride gives N-acetyl pyrrole.
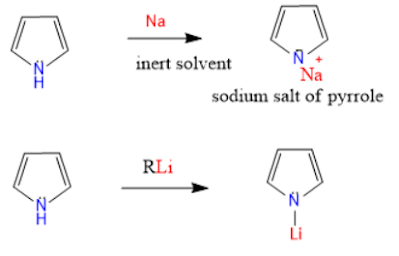
7. N-Metallation: Metallation takes place at Nitrogen in pyrrole.
Oxidation:
- Pyrrole oxidized with hydrogen peroxide and dihydropyran (DHP) gives 1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrole-2-one.
- Pyrrole is oxidised by chromium trioxide in sulphuric acid to give maleic imide.
Reduction:
- Pyrrole reduced with platinum and H2 give pyrrolidine.
- Pyrrole reduced with zinc in acetic acid give 2,5-dihydro pyrrole.
ReimerTiemann reaction: pyrrole undergo Reimer Tiemann reaction to give 3-chloropyridine.
Medicinal uses:
Drugs containing a pyrrole ring:
1. Tolmetin is an NSAID drug used to treat pain, swelling, and tenderness in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis conditions.
2. Atorvastatin is an anti-hyperlipidemic and used to treat cardiovascular diseases.
3. Pyrrolnitrin is used as an anti-fungal antibiotic.
4. Ketorolac is an NSAID drug used to treat moderate to severe pain.
References (Latest editions):
Heterocyclic chemistry by Raj K. Bansal.
Heterocyclic chemistry by T.L. Gilchrist.
Organic chemistry by Morrison and Boyd.
A textbook of organic chemistry - Arun Bahl. B.S. Bahl.































Hai sir I had known about you.....that you are all india G-PAT 200 RANKER...I Hope your notes will be usefull to all B.Pharm and M.Pharm students....tq vry much sir for creating new blog to pharmacy students
ReplyDelete