Synthesis, Reactions and Medicinal Uses of Thiophene
Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Thiophene
Thiophene is a five-membered heterocyclic compound having one Sulphur atom as a heteroatom.
Physical properties:
Colour : colorless
State : liquid
Boiling point : 84 oC
Melting point : -38 oC
Solubility : Insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents
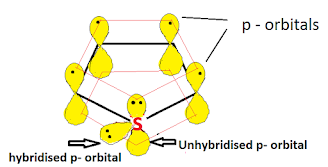
Structure & Aromaticity:
All atoms in the thiophene ring are sp2 hybridised, so the thiophene contains a planar ring structure. the sp2 hybrid orbitals overlap with each other and with "s" atomic orbital of the five hydrogens forming C-C, C-S, and C-H sigma bonds. all these sigma bonds lie in one plane.
Thiophene also has unhybridized p orbitals and these are perpendicular to the plane of the ring. each p orbital on carbon atom contains one electron and the p orbital on sulfur contains lone pair of electrons(two electrons). the p orbital overlap to form delocalized pi molecular orbital. thiophene shows aromaticity because the resulting pi molecular orbital (which contain 6 electrons) satisfies the Huckel's rule (n=1 in 4n+2).
Resonance structures:
1. From sodium succinate: Heating of sodium succinate with phosphorous trisulphide gives thiophene.
2. From n-butane: n-butane is heated with sulfur at high-temperature yields thiophene.
3. Hinsberg thiophene synthesis: Reaction between α-diketones and thiodiacetate gives substituted thiophenes.
4. Paal-Knorr synthesis: Condensation of 1,4- Dicarbonyl compounds with phosphorous pentasulphide give thiophene.
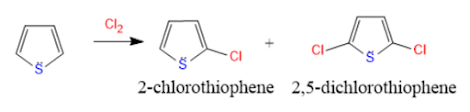
Electrophilic substitution reactions:
Electrophile attack at 2nd position gives more resonance structures than electrophile attack at the 3rd position. More resonance structures mean more stable it is.
So, electrophilic substitution reactions take place 2nd position in thiophene.
1. Halogenation: Thiophene reacts with halogens to give 2-halo thiophene and 2,5-dihalothiophene.
2. Nitration: Thiophene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in acetic acid gives 2-nitrothiophene.
4. Acylation: Thiophene reacts with Acetic anhydride and lewis acid as catalyst give 2-Acylthiophene.
5. Alkylation: Thiophene reacts alkyl halide and lewis acid give 2-alkylthiophene.
Other reactions:
Reduction: Thiophene is reduced with molecular hydrogen and palladium gives Tetrahydrothiophene.
If thiophene is reduced with molecular hydrogen and nickel gives n-butane.
Oxidation: Thiophene treated with trifluoroperacetic acid give thiophene-s-oxide as an intermediate which undergoes Dields alder type of reaction to give sulfoxide and sulfone products.
Reaction with Organometallic compounds: Thiophene is reacted with organolithium which gives 2-thiophenyllithium which upon treated with carbon dioxide and subsequent hydrolysis gives thiophene-2-carboxylic acid.
Polymerization reaction: Thiophene is reacted with hot phosphoric acid to give trimer.
Medicinal uses:
Drugs that contain a Thiophene ring:
1. Tiagabine is an anticonvulsant agent, used to treat epilepsy.
2. Methapyrilene is antihistaminic used to treat allergic rhinitis. Methapyrilene has strong sedative action so it is also used to insomnia.
3. Suprofen is an NSAID drug used to treat mild to moderate pain.
4. Cephalothin is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections.
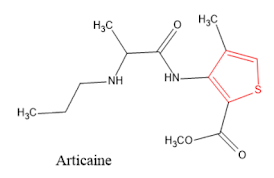
5. Articaine is a local anesthetic agent.
6. Sitaxsentan is cardiovascular agent used in the management of pulmonary artery hypertension.
References (Latest editions):
Heterocyclic chemistry by Raj K. Bansal.
Heterocyclic chemistry by T.L. Gilchrist.
Organic chemistry by Morrison and Boyd.
A textbook of organic chemistry - Arun Bahl. B.S. Bahl.





























Comments
Post a Comment