Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Isoquinoline
Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Isoquinoline
Isoquinoline is a bicyclic hetero-aromatic compound having nitrogen at the second position as heteroatom. It is also called benzo[c]pyridine, the benzene is fused with the "c" side of pyridine. another name for isoquinoline is 2-azanaphthalene.
Physical properties:
Colour: colourless
State: liquid
Melting point: 26 - 28 oC
Boiling point: 242 oC
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water and soluble in organic liquids and dilute acids.
Structure and Aromaticity:
All atoms in Isoquinoline are sp2 hybridised and have a planar structure. Unhybridised p-orbitals sidewise overlap to form five pi bonds. Isoquinoline contains a total of ten delocalised pi electrons, following the huckles rule hence quinoline is an Aromatic.
Resonance structures:
Synthesis of Isoquinoline:
1. Bischler-Napieralski synthesis:
2-aryl ethanamines react with acyl chloride to give an amide, which upon treated with phosphorus pentoxide or phosphorus oxychloride with loss of water gives 3,4-dihydro isoquinoline. which upon reduction to give isoquinoline derivative.
2. Pictet-Grams synthesis:
It is the modification of the Bischler-Napieralski reaction, in which 2-hydroxy-2-aryl ethanamines treated with acyl chlorides give amide derivative, which under the presence of phosphorus oxychloride cyclized and dehydrated to give isoquinoline derivative.
3. Pomeranz-Fritsch synthesis:
Condensation of aryl aldehyde with aminoacetal to form an aryl-aldmine. Then it is treated with strong acid caused protonation and cause elimination of alcohol and the formed electrophile attacks at the aromatic ring as electrophile. The final elimination of another alcohol yields Isoquinoline.
Electrophilic addition reactions at "N" atom of Isoquinoline:
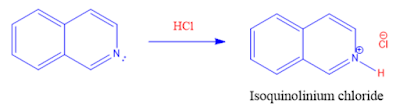
1. Reaction with acids (Protonation):
Isoquinoline reacts with acids to form Isoquinolinium salts.
2. N-Alkylation:
Isoquinolines react with alkyl halides to form Isoquinoline-N-alkyl halide.
3. N-Acylation:
Isoquinoline reacts with Acyl halides to form Isoquinoline-N-acyl halide.
Electrophilic Substitution Reactions:
Electrophilic substitution reactions occur at the 5th (major) and 8th (minor) positions.
1. Nitration:
Isoquinoline reacts with Nitric acid and sulphuric acid to give 5 and 8 nitro Isoquinoline.
2. Sulphonation:
Isoquinoline reacts with conc. sulphuric acid and/or Oleum to Isoquinoline-5-sulphonic acid and Isoquinoline-8-sulphonic acid.
3. Halogenation:
Isoquinoline reacts with halogens in lewis acids to give 5 and 8 halo derivatives.
Oxidation reactions:
1. Isoquinoline oxidised with alkaline KMnO4 to give Phthalic acid and Pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylic acid.
2. Isoquinoline oxidised with neutral KMnO4 to give Phthalimide.
Reduction reactions:
1. Isoquinoline reduced with diethyl aluminium hydride or Na in Liq. Ammonia to give 1,2-dihydro isoquinoline.
2. Isoquinoline reduced with Na in ethanol or H2-pt in methanol gives 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline.
3. Isoquinoline reduced with H2-pt in Conc.HCl to give 5,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinoline.
Nucleophilic substitution reaction:
Isoquinoline reacts with sodamide in ammonia at high temperature to 1-amino isoquinoline.
Drugs containing Isoquinoline ring:
1. Papaverine acts as an antispasmodic(smooth muscle relaxant). it is also a vasodilator, used to improve blood flow in patients with circulation problems.
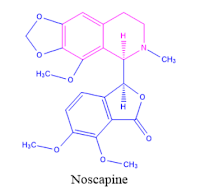
2. Narcotine (Noscapine) is an antitussive agent used as a cough suppressant.
3. Emetine is used to induce vomiting and also it acts as an antiprotozoal agent.
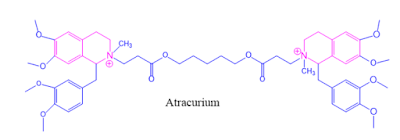
4. Atracurium and Doxacurium act as Neuromuscular blocking agents.
5. Quinapril is an ACE inhibitor used to treat hypertension.
References (Latest editions):
Heterocyclic chemistry by Raj K. Bansal.
Heterocyclic chemistry by T.L. Gilchrist.
Organic chemistry by Morrison and Boyd.
A textbook of organic chemistry - Arun Bahl. B.S. Bahl.


























Comments
Post a Comment