Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Pyrazole
Synthesis, Reactions, and Medicinal Uses of Pyrazole
Pyrazole is a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic compound containing two adjacent nitrogen atoms at 1 and 2 positions.
Physical properties:
Colour : colorless
State : solid
Boiling point : 186 - 188 oC
Melting point : 66 - 70 oC
Solubility : soluble in hot water, soluble in organic solvents.
Structure & Aromaticity:
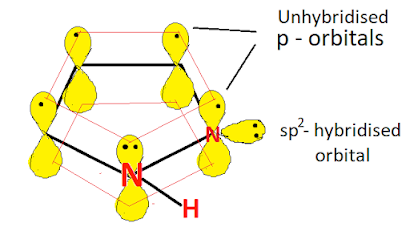
All atoms in the pyrrole ring are sp2 hybridised, so the pyrrole contains a planar ring structure. the sp2 hybrid orbitals overlap with each other and with "s" atomic orbital of the four hydrogens forming C-C, C-N, C-H, and N-H sigma bonds. all these sigma bonds lie in one plane.
Pyrazole also has unhybridized p orbitals and these are perpendicular to the plane of the ring. each p orbital on carbon atom contains one electron and the p orbital on nitrogen contains lone pair of electrons(two electrons). the p orbital overlap to form delocalized pi molecular orbital. Pyrazole shows aromaticity because the resulting pi molecular orbital (which contain 6 electrons) satisfies the Huckel's rule (n=1 in 4n+2).
Resonance structures:
Tautomerism:
Hydrogen atom migrates rapidly from one nitrogen to other nitrogen.
Synthesis:
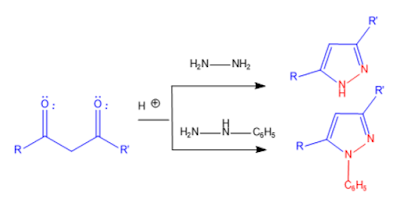
1. knorr pyrazole synthesis: 1,3-dicarbonyl compound reacts with hydrazine or its derivatives in the presence of acid catalyst gives 3,5-substituted pyrazole derivatives.
2. From Diazo compound: Addition of diazo compound to acetylenic derivatives gives pyrazole.
3. From Pyramidine: Pyramidine reacts with hot hydrazine solution gives pyrazole.
Mechanism:
Electrophilic substitution reactions:
Electrophilic attack at C-3 and C-5 gives unstable intermediates, electrophilic attack at C-4 gives the stable product.
1.Nitration: Pyrazole reacts with Nitrating mixture gives 4-nitro pyrazole
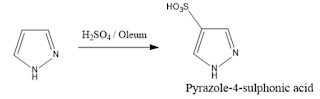
2. Sulphonation: Pyrazole reacts with sulphuric acid in oleum gives pyrazole-4-sulphonic acid
3. Halogenation: Pyrazole reacts with halogens in presence of lewis acids gives 4-halo pyrazole
4. N-alkylation: Pyrazole reacts with alkyl halides give N-alkyl pyrazole.
5. N-acylation: pyrazole reacts with acetyl chloride gives N-acetyl pyrazole.
Electrophilic reactions are readily taking place in neutral and basic media. In acidic media, pyrazole is protonated and resistant to further electrophilic reactions.
Oxidation: Pyrazole ring is stable towards oxidation reaction, but substitutes present on ring gets oxidised
Reduction: Pyrazole reduced under lower temperature to give 4,5-Dihydro-pyrazole, under higher temperature to give pyrazolidine.
Medicinal uses:
Drugs containing pyrazole ring:
1. Antipyrine: Used as Analgesic (relieve pain) And Antipyretic(decrease body temperature.
2. Analgin: Used as Analgesic and Antipyretic.
3. Phenylbutazone: Used as an Analgesic, Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory agent.
4. Oxybutazone: Used as an Analgesic, Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory agent.
5. Celecoxib: Used as an Analgesic, Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory agent.
References (Latest editions):
Heterocyclic chemistry by Raj K. Bansal.
Heterocyclic chemistry by T.L. Gilchrist.
Organic chemistry by Morrison and Boyd.
A textbook of organic chemistry - Arun Bahl. B.S. Bahl.


























Comments
Post a Comment